Bitcoin
Ownership
Private key k is 256 bits or 32 bytes, a huge number, generated randomly1, for example:
c058c9248b784d9f9664a28eec87c30bb19e00beb33701ae4c414d099f34b533
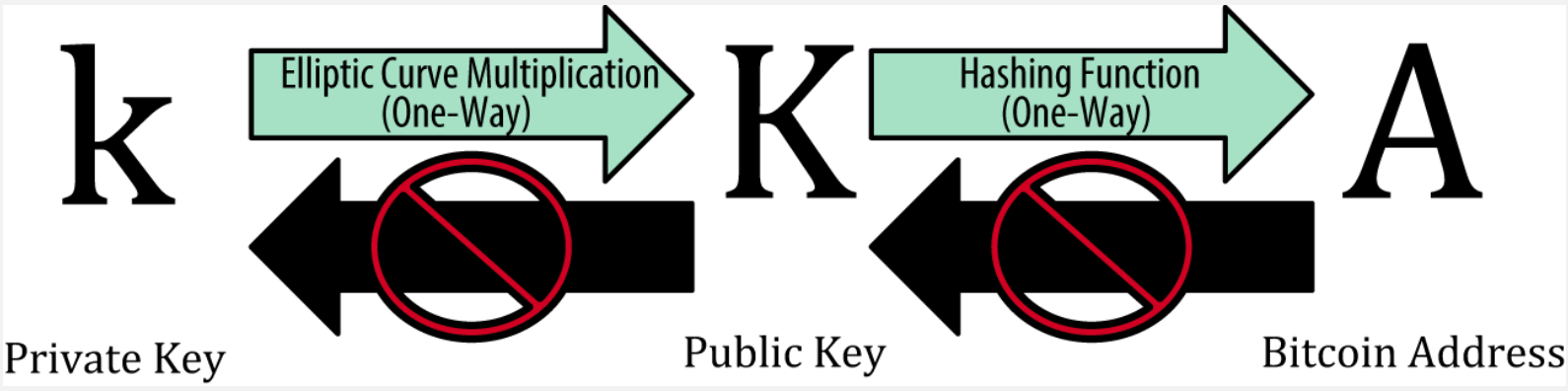
Public key K can be derived from the private key k. A bitcoin address A can be derived from the public key K. Deriving keys in the opposite direction is not possible2.
A is generated using SHA256 hashing and then Base58 encoding.
Wallets
Wallet holds and manages the keys.
- Non-deterministic - a bunch of unrelated keys, each key requires a separate backup
- Deterministic(HD) - seed → deterministic keys, only a seed requires a backup
Balance of a wallet is a sum of unspent transaction outputs that the wallet can unlock.
1 BTC = 108 Satoshi
Blocks and Transactions
Bitcoin is a UTXO-based blockchain.

Blocks contain transactions, transactions contain inputs(vins) and outputs(vouts).
- Red - spent transaction outputs
- Green - unspent transaction outputs
Blocks are generated every 10 minutes
Block size is 1 mb, SegWit softfork allows up to 3 mb of signatures and scripts, which are now not counted towards the original 1 mb block size
Transaction size is ~300 bytes
Transaction Explained

This example tx has 1 vin and 2 vouts.
vin contains a witness — a script, which proves the ownership of the funds
vouts have the type — P2SH and P2PKH and corresponding witness scripts or encumbrance, which need to be solved to spend them
Spending a UTXO
Having a simple encumbrance:
3 OP_ADD 5 OP_EQUAL
The witness(solution) will be:
2
Which results to:
2 3 OP_ADD 5 OP_EQUAL
The Bitcoin Script language uses opcodes and a stack, see the execution:

If the script execution leaves true as a result — it means that the witness is correct and allowed to spend the funds on that vout.
The Bitcoin Script language is not Turing complete, there are no loops, only simple conditional statements. This means, that in contrary to the Ethereum VM, the programs are finite and can't be used in a denial of service attack against the Bitcoin network, since this program is executed on every Bitcoin node.
P2PKH - Pay to Public Key Hash
P2PKH is the simplest type of encumbrance:
OP_DUP OP_HASH160 <Pubkey Hash> OP_EQUALVERIFY OP_CHECKSIG
The witness must be presented in a form of:
<Signature> <Pubkey>
Result:
<Signature> <Pubkey> OP_DUP OP_HASH160 <Pubkey Hash> OP_EQUALVERIFY OP_CHECKSIG

The witness presents his <Pubkey> and a <Signature> which can only be generated by the corresponding private key k. The posession of k is a proof of the vout ownership.
P2SH - Pay to Script Hash
The most popular P2SH example is a multisig, encumbrance:
HASH160 <20-byte hash of redeem script> EQUAL
The witness:
2 <Pubkey1> <Pubkey2> <Pubkey3> 3 CHECKMULTISIG
Result:
0 <Sig1> <Sig2> 2 <Pubkey1> <Pubkey2> <Pubkey3> 3 CHECKMULTISIG HASH160 <20-byte hash of redeem script> EQUAL
This encumbrance requires 2 signatures from any 2 out of 3 <Pubkey> owners to be present to unlock the vout.
Address Types
1... - P2PKH
3... - P2SH
bc1q... - P2WPKH(SegWit / Bech32)
bc1p... - P2TR(Taproot)
Mining
- Validates transactions
- Includes transactions in a block
- Adds a coinbase transaction, a reward to a miner
- Adds a fingerprint of the last block
Current reward is 6.25 BTC.
6 confirmations are considered irrevocable.